How Does Google Search Work?
go.ncsu.edu/readext?995221
en Español / em Português
El inglés es el idioma de control de esta página. En la medida en que haya algún conflicto entre la traducción al inglés y la traducción, el inglés prevalece.
Al hacer clic en el enlace de traducción se activa un servicio de traducción gratuito para convertir la página al español. Al igual que con cualquier traducción por Internet, la conversión no es sensible al contexto y puede que no traduzca el texto en su significado original. NC State Extension no garantiza la exactitud del texto traducido. Por favor, tenga en cuenta que algunas aplicaciones y/o servicios pueden no funcionar como se espera cuando se traducen.
Português
Inglês é o idioma de controle desta página. Na medida que haja algum conflito entre o texto original em Inglês e a tradução, o Inglês prevalece.
Ao clicar no link de tradução, um serviço gratuito de tradução será ativado para converter a página para o Português. Como em qualquer tradução pela internet, a conversão não é sensivel ao contexto e pode não ocorrer a tradução para o significado orginal. O serviço de Extensão da Carolina do Norte (NC State Extension) não garante a exatidão do texto traduzido. Por favor, observe que algumas funções ou serviços podem não funcionar como esperado após a tradução.
English
English is the controlling language of this page. To the extent there is any conflict between the English text and the translation, English controls.
Clicking on the translation link activates a free translation service to convert the page to Spanish. As with any Internet translation, the conversion is not context-sensitive and may not translate the text to its original meaning. NC State Extension does not guarantee the accuracy of the translated text. Please note that some applications and/or services may not function as expected when translated.
Collapse ▲How many times a day do you find yourself reaching for your phone to quickly Google a question and find an answer to a pressing question? Using Google or other popular search engines like Microsoft’s Bing or DuckDuckGo is a quick and easy way to solve many problems in the modern world. But have you ever wondered how the Google search engine finds the answers it provides to you?
The Search Engine
Google’s search engine uses a three-step process to provide the most relevant and accurate responses to a search query. First, it uses natural language processing to break down your query and understand your meaning. Second, it uses a crawler to trawl the web and collect information on many websites. It stores that information in a giant online index, which is kind of like a digital filing cabinet for web pages. Finally, it uses an algorithm to pull relevant results that match your query and list them in order of most relevant to least relevant for you to peruse.
The Query
A query is what you type into the search box. You can Google almost anything, from how to cook crawfish to what hairstyle a popular actress wore during an awards ceremony.
Most of the time, your query will likely match other questions people have searched on Google previously. In this case, you will see a drop-down menu appear below the search box with autocomplete suggestions of possible queries you may want to select that have some similarity to yours.
When your query is entirely original, Google uses its language processing system to understand what you mean. Natural Language Processing, or NLP, is an AI system that allows computing devices to understand and generate both text and speech. IBM explains more about Natural Language Processing if you want to read more.
Human language is often vague and layered. Sometimes you may know exactly what you want to ask, like “What is the name of the fish with orange strips?” Other times, you may not recall exactly what you wanted and may find yourself Googling around the subject, with queries like “animal in water orange and white.” In this case, Google’s Natural Language Processing system will interpret what you mean.
This also means that Google can correctly interpret many spelling mistakes, which is good news if you struggle to remember if the word “refrigerator” has the letter d somewhere in the middle of the word!
The Crawler and the Index
Google uses a crawler called the Googlebot to keep tabs on online content. Other popular search engines use similar tools. So, what does the Googlebot do?
The Googlebot scans websites by progressing from one link to another and checking for keyword-based content. Suppose a popular sports website adds a new page about baseball, linked to its homepage about sports. The Googlebot will see the link on the original sport-related homepage, and check out the new page via the link.
Many websites use something called a sitemap that lists the URLs of all their pages to make sure the Googlebot can easily find each one.
Information like the URL, keywords, locations, and the quality of a website gets stored in Google’s index. This is like a digital file folder keeping information about all the websites the crawler has explored.
The Algorithm and Ranked Search Results
Google does not dump all the results of its index on you higgledy-piggledy when you type in a query. Instead, it carefully ranks the websites it determines will best answer your question or fit your needs and places the most useful results at the top of the page of search results.
To do this, the Google search engine uses a powerful algorithm. An algorithm is basically a list of instructions designed to accomplish a set task. In this case, Google’s algorithm pulls possible websites from its index and ranks them based on many factors, including which websites best match the keywords you used in your query, the physical location of a business listed on a website, and the quality and organization of the website. The algorithm also considers two important elements of website quality: whether or not the website is mobile-friendly, and how quickly the website loads.
Another factor that can impact the ranking of a website in a Google search is the quality of images on the website because a Google search does not just consider text–it also searches images and videos. Factors like freshness of content, as opposed to older and outdated content, also play a role in ranking.
Your geographic location can also impact how the Google algorithm ranks results. If you search for “best pancakes” while in Florida, you will get a list of diners and restaurants located in Florida. But if you type in the same query while you are in Maine, you will see a completely different list of restaurants.
The Elements of a Google Search
The layout of a search result page may look different depending on the kind of query you use. Understanding the elements of common Google search result layouts can help you quickly navigate to the answer you want. It is worth noting that these elements do change over time. You can read more about how Google chooses to lay out search results here.
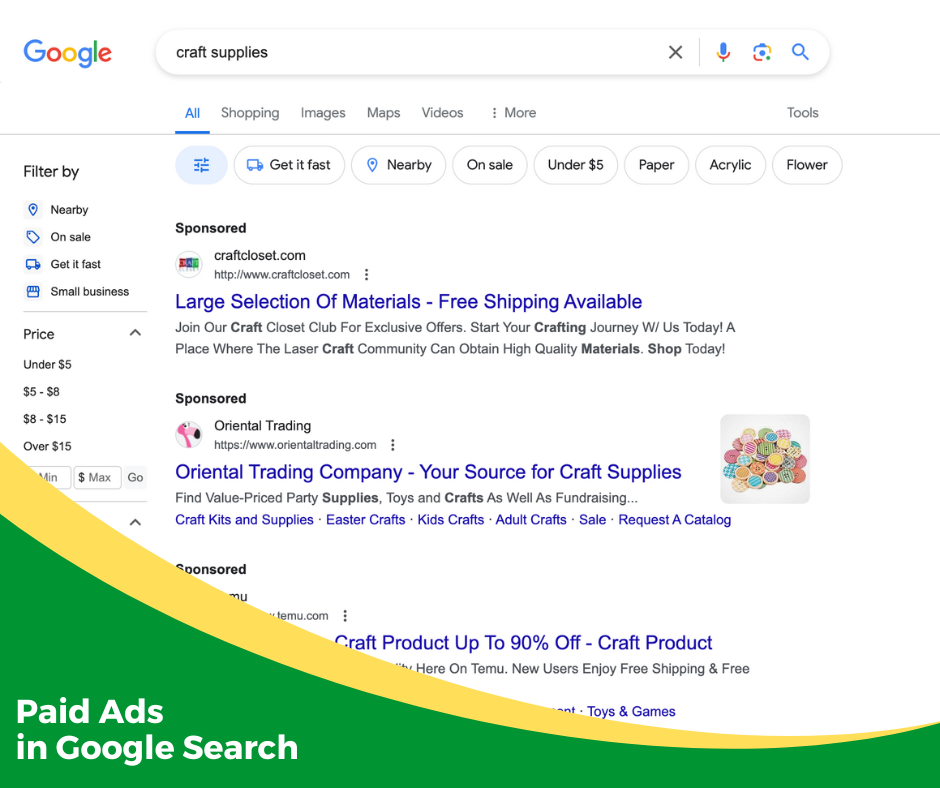
Ads Vs Organic Content
Often the top and bottom results in your Google search results page will list paid ads instead of organic search results. This means that a company or entity has entered an auction to have an ad displayed for any queries using certain keywords. Often these ads use a “pay-per-click” model, meaning that the company only has to pay for the promotion when someone clicks on the ad.
Google lets you know which of the results on the search results page are paid ads by placing the word “Sponsored” above the headline of the ad in the search results.
It is worth noting that Google ranks ads based on the quality of the ad, the landing page it links to, and several other factors. However, the ads still appear at the top of the page because the company paid for that privilege, not because that result is necessarily the best option for you.
Organic search results, in contrast, are search results selected and ranked based on how well they meet the Google algorithm’s metrics for relevance and quality. These websites have not paid to receive their place in the ranking. They simply match what you are looking for.
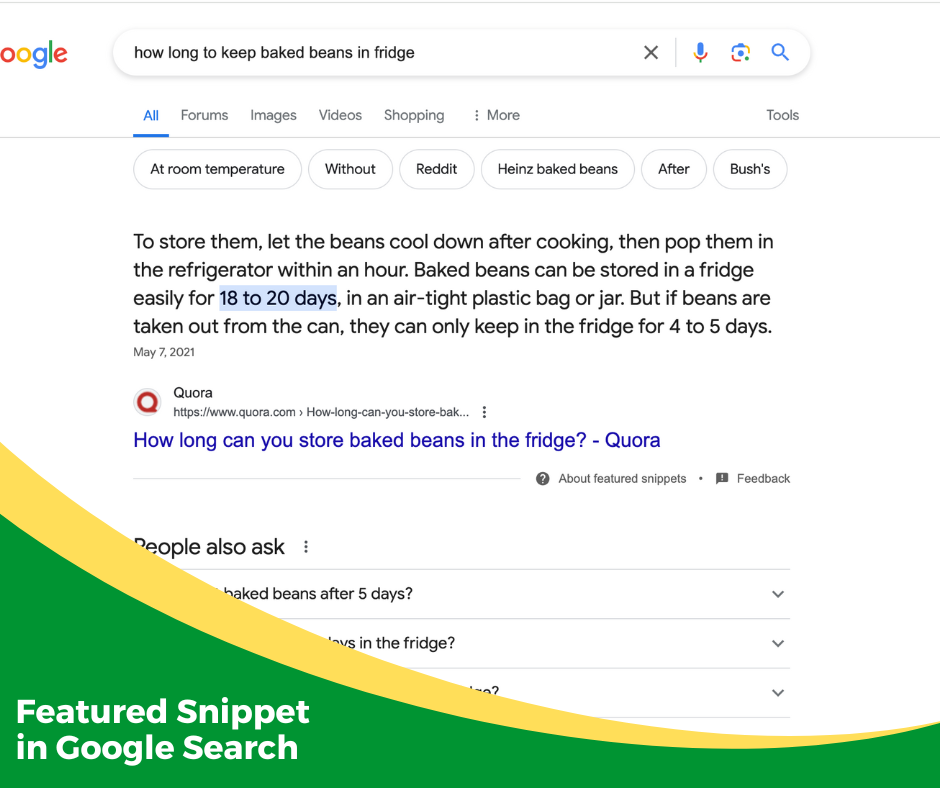
Featured Snippet
Sometimes, your Google search results page will place a snippet of information pulled from a relevant website right at the top of the search results. This highlighted text often briefly and thoroughly answers a specific question you asked in your query. Google calls this a “featured snippet.”
While the featured snippet is a handy tool, you should always check the parent website to see where the snippet came from, and assess the reliability of the answer yourself. For example, medical information that comes from the Mayo Clinic is a lot more reliable than information that comes from a company selling medicine.
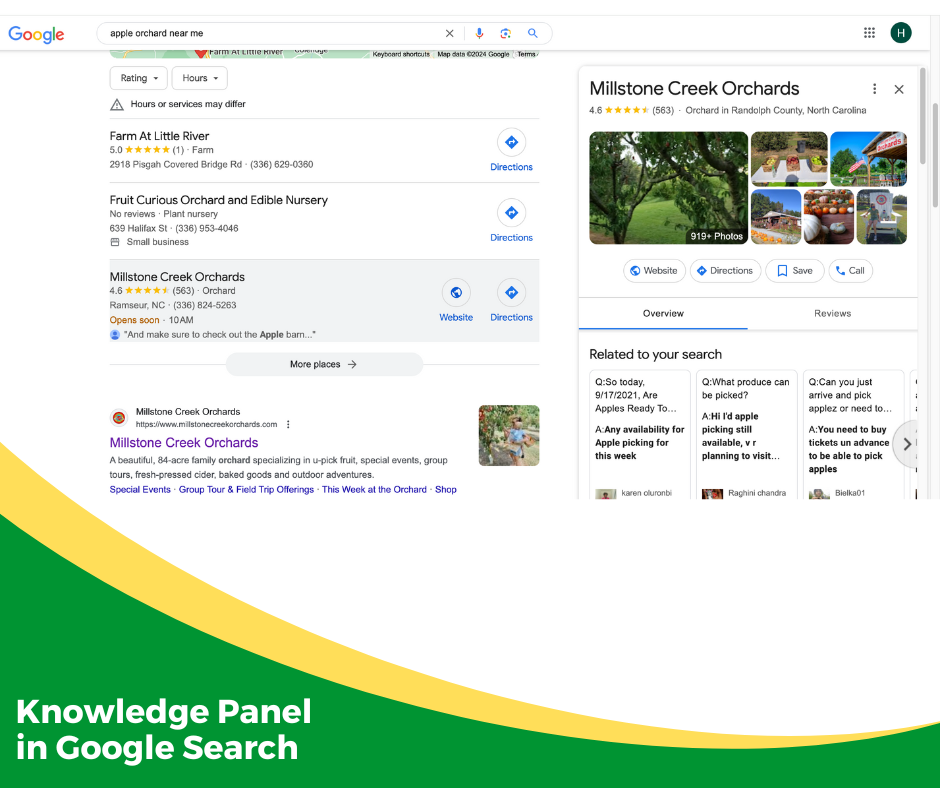
Google Knowledge Panel
Another handy element you may see on a Google search results page is something Google calls a “knowledge panel.” One example of a knowledge panel is the sidebar of information that pops up when you query anything about a business, and Google provides the Google Business Profile of that company with an address, phone number, ratings, and more.
The knowledge panel often includes interactive extensions like the ability to tap on the phone number and make a call if you are on your phone.
Google also provides calculators or convertors at the top of the search results page when you query a question like “What is 2 +2” or “How many feet in three yards.”
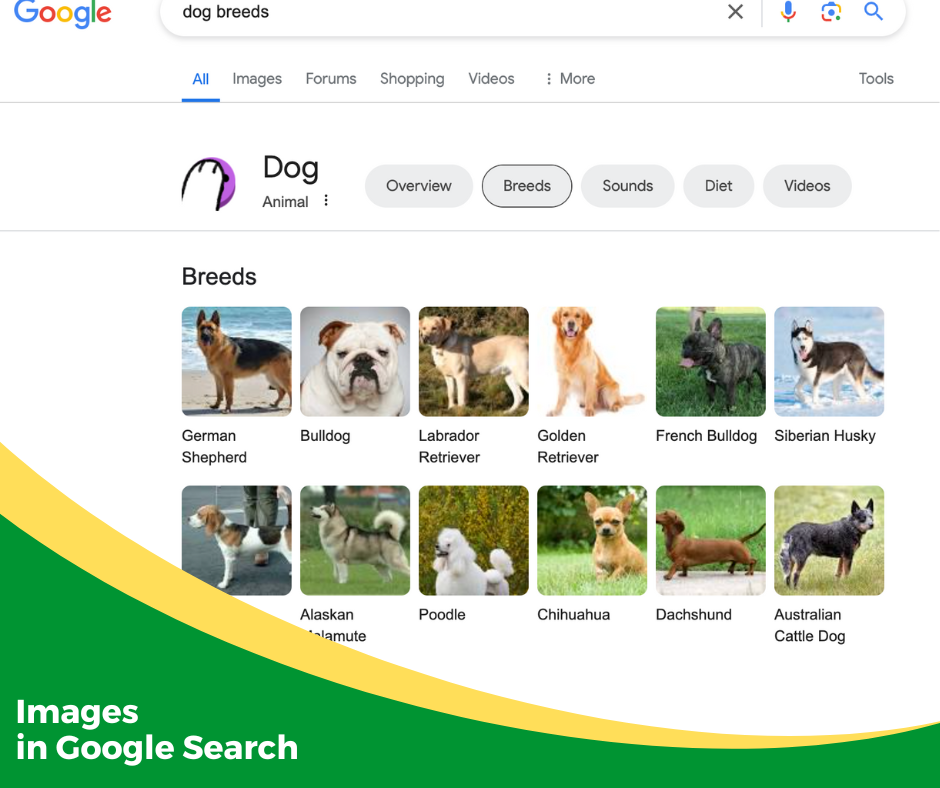
Image Results
Depending on what you queried, Google may determine that an image or a video (such as a YouTube video) can provide the best answer. Videos and images in the search results are called “rich results,” meaning that they add extra elements to the search results page.
If you do not find the image you want on the Google search results page, you can select “images” below the search box to see just images based on your query.
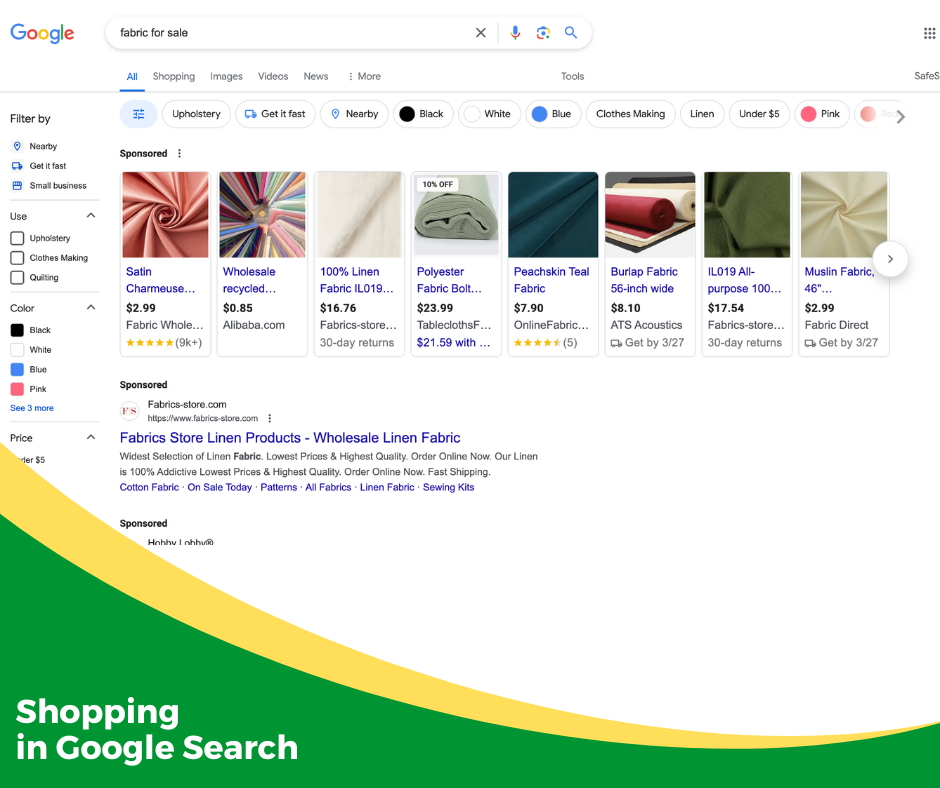
Sale Query
When you Google something like “best mattress” or “fabric for sale,” the Google search results page will often place a river of shopping options at the top of the screen. This allows you to quickly compare brands and prices offering the item you want. Below that, you can scroll down through the organic search options that provide the websites of the online shops most likely to provide what you want.
Just like with images, you can also select “shopping” below the search box if you want to exclusively see items available for purchase in response to your query.
Learning More About Google Search
If you want to learn more about how to use Google’s search engine most effectively, you can check out GCFGlobal’s online learning tips. You can also call the Randolph County Cooperative Extension office (336-318-6002) to schedule a free in-person tech help session with a Digital Skills Agent.